


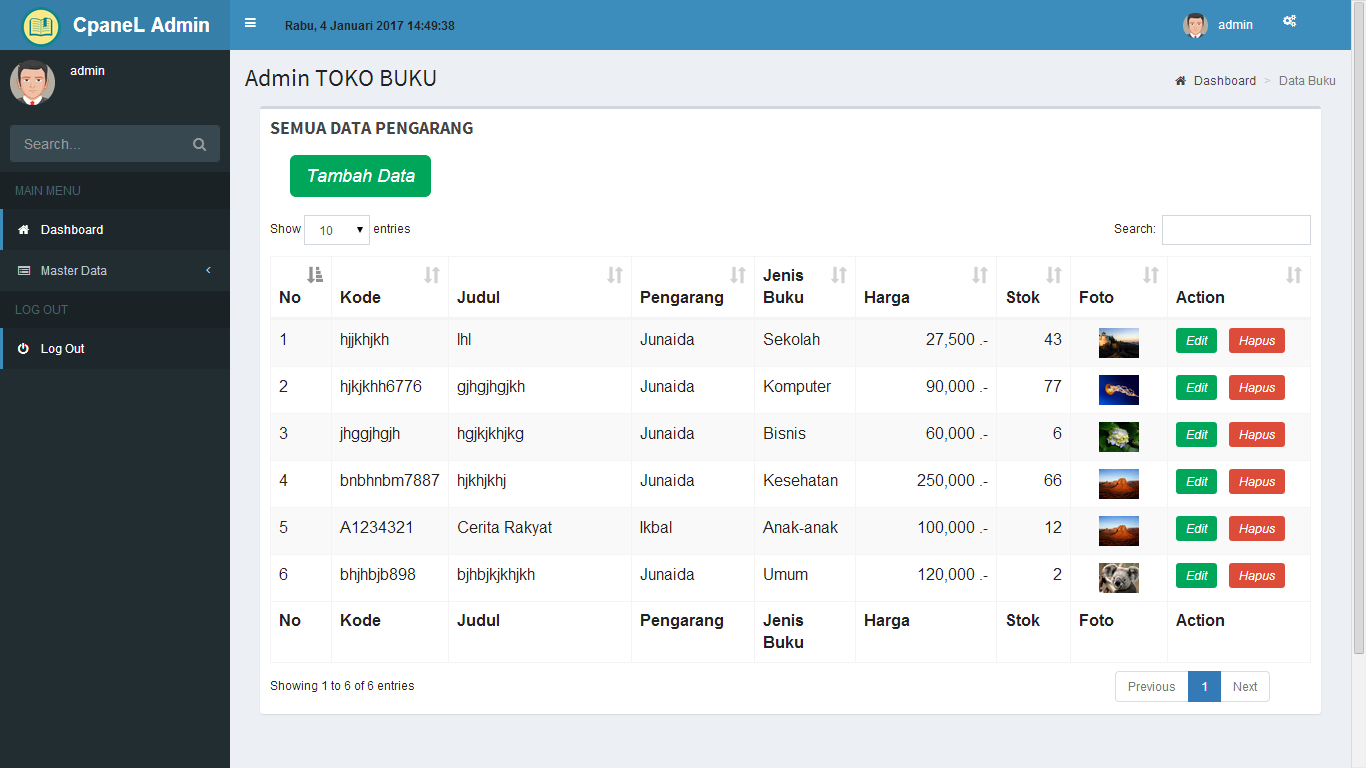
- #DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG UPDATE#
- #DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG MANUAL#
- #DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG LICENSE#
The data entry and computer programs are the physical trail.The data are stored in magnetic files.
#DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG MANUAL#
The audit trail is less observable in computer-based systems than traditional manual systems. If necessary, confirm these source documents by contacting the customers.Īccounting Records in a Computer-Based SystemĪccountants should be able to trace in both directions.Sampling and confirmation are two common techniques.Īccounts Receivable Control Account-General LedgerĪccounts Receivable Subsidiary Ledger(sum of all customers receivables)Įxample of Tracing an Audit TrailVerifying Accounts Receivable From these journal entries, identify source documents that can be pulled from their files and verified.
#DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG UPDATE#
Select a sample of update entries made to accounts in the AR subsidiary ledgerand trace these to transactions in the sales journal (archive file).4.
Reconcile the AR control figure with the AR subsidiary account total.3. Compare the AR balance in the balance sheet with the master file AR control account balance.2. General LedgerControl Accounts Accounts Receivable Inventory Cost of Goods Sold Salesġ.
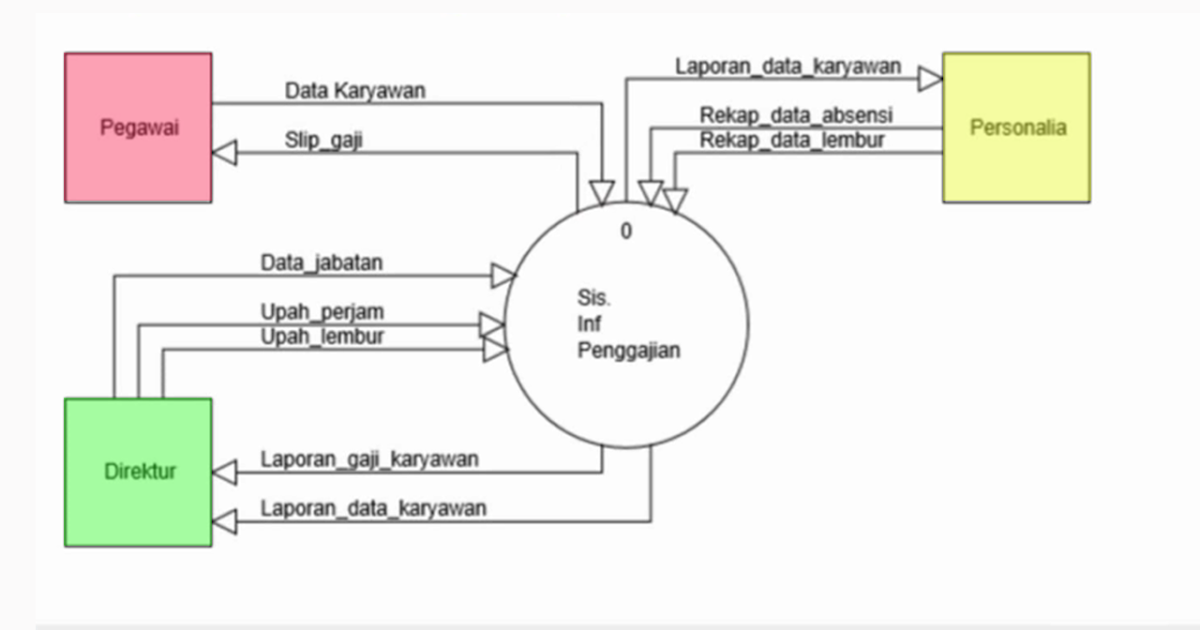
Gambar Formulir Ayat Jurnal (atas) dan Buku Besar (bawah)įlow of Info from the Economic Events Into the General Ledger Ledger - a book of financial accounts general ledger - shows activity for each account listed on the chart of accountssubsidiary ledger - shows activity by detail for each account type Special journals - specific classes of transactions that occur in high frequencygeneral journal - nonrecurring, infrequent, and dissimilar transactions Manual Systems (2)Journals - a record of chronological entry Source Documents - used to capture and formalize transaction data needed for transaction processingProduct Documents - the result of transaction processingTurnaround Documents - a product document of one system that becomes a source document for another system Physical component (sales order processing)financial component (cash receipts) Revenue Cycle: time lag between the two due to credit relations with customers : Physical component (acquisition of goods)financial component (cash disbursements to the supplier)Ĭonversion Cycle :the production system (planning, scheduling, and control of the physical product through the manufacturing process)the cost accounting system (monitors the flow of cost information related to production) Production Planning and ControlCost AccountingĮachCyclehasTwoSubsystemsExpenditure Cycle: time lag between the two due to credit relations with suppliers: Purchasing/Accounts PayableCash DisbursementsPayrollFixed Assets The expenditure cycle,the conversion cycle, andthe revenue cycle.Įxpenditure Cycle Conversion Cycle Revenue Cycle ObjectivesforChapter2Broad objectives of transaction cyclesTypes of transactions processed by each of the three transaction cyclesThe basic accounting records used in TPSThe traditional accounting records and their magnetic equivalents Documentation techniquesBatch and real-time processing and the impact of these technologies on transaction processingĪ Final Transaction isan economic event that affects the assets and equities of the firm, is reflected in its accounts, and is measured in monetary terms.similar types of transactions are grouped together into three transaction cycles:
#DFD SISTEM INFORMASI PENJUALAN BARANG LICENSE#
Cengage Learning and South-Western are trademarks used herein under license COPYRIGHT 2009 South-Western, a division of Cengage Learning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
